Transclude of Biolayer-interferometry-and-its-applications-in-drug-discovery-and-development---ScienceDirect-(4_23_2025-1:52:06-PM)
SPR = surface plasmon resonance
Uses
- kinetic analyses
- analyte detection
- quantitation with mid-high throughput
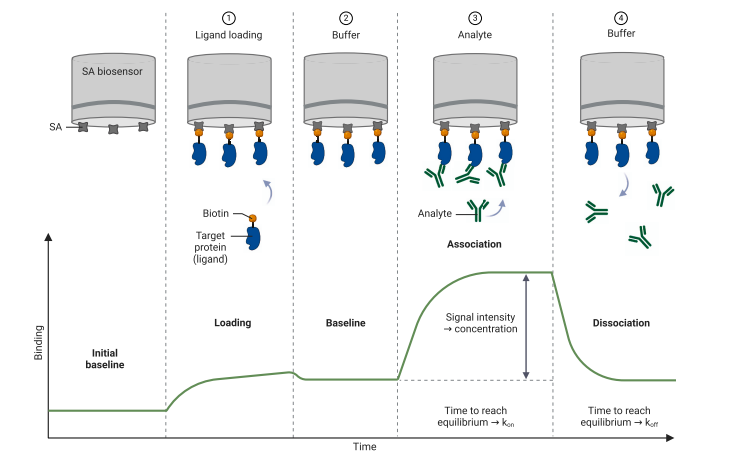
kon and koff = part of Kd calculations with BLI and SPR
Advantages of BLI
- no molecule labels - less steps in the essay, less interference
- variety of different sensors tailored to different uses
- the refractive index or viscosity of the sample does not affect measurement
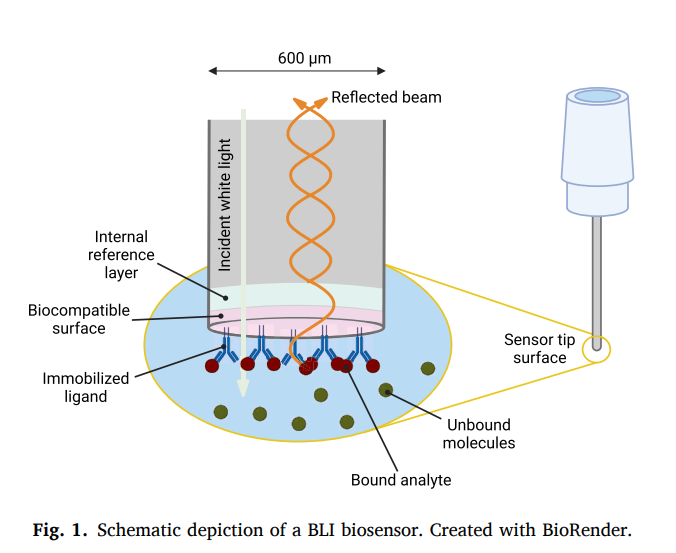
- Change in thickness of the layer on the sensor tip after binding accuses a change on the sensor tip
- wavelength shift occurs - reported in real time
Why BLI over Micro-scale thermophoresis - MST
- MST requires protein labelling
- Binding information is limited only to a Kd value
BLI experiment troubleshooting
- In solution affinity determination - nothing is immobilized
- binder and protein reach equilibrium
- Biosensors are added which can capture free protein - measure how much was unbound
- Do this with increasing amounts of binder - see how much free target is left every time
- Degree of binding
- if less free protein - the binder binds to target protein strongly - low signal
- if more free protein - the binder binds to target protein weakly - high signal
- Limitations of this method
- interactions at or below Kd can be measured - only for strong binders
Crowding on the biosensor affects values - mitigated by using a 3D sensor
Non-specific sensor binding
- high concentrations of analyte are used - up to 10*Kd value
- this can cause colloidal aggregates to form on the biosensor - increasing signal improperly
- a separate sensor without the ligand is used - or ligand analogue - this will experience signal only due to the crowding - and is subtracted from the main signal
- must use detergents or additives to stop